Reinke’s Edema (Polypoid Corditis)
Reinke’s edema is a condition caused by the accumulation of gelatinous fluid in the Reinke’s space of the vocal cords. It typically presents with symptoms such as vocal deepening, hoarseness, and vocal fatigue. The most common causes include smoking, reflux disease, and improper or excessive voice use.
What Are the Symptoms of Reinke’s Edema?
- Vocal Deepening: Female patients often complain of being mistaken for having a male voice.
- Hoarseness and Roughness: Persistent voice loss and a muffled voice are noticeable.
- Throat Discomfort: Patients frequently feel the need to clear their throat.
- Vocal Fatigue: Progressive vocal weakness and fatigue throughout the day are common.
- Shortness of Breath: In advanced cases, edema on the vocal cords may cause breathing difficulties.
Causes of Reinke’s Edema
Reinke’s edema can result from various factors. The most common causes include:
- Smoking: One of the biggest risk factors. Tobacco smoke causes chronic irritation of the vocal cords, leading to edema formation.
- Reflux Disease: Stomach acid refluxing into the esophagus and throat may irritate the vocal cords.
- Improper or Excessive Voice Use: Shouting, speaking loudly, or singing for prolonged periods can cause irritation to the vocal cords.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal disorders such as hypothyroidism can also trigger edema formation.
Diagnosis and Evaluation Process
Reinke’s edema is diagnosed through videolaryngoscopy performed by an ENT specialist. With this imaging method, patients can see their own vocal cords on screen, and the size of the edema can be evaluated.
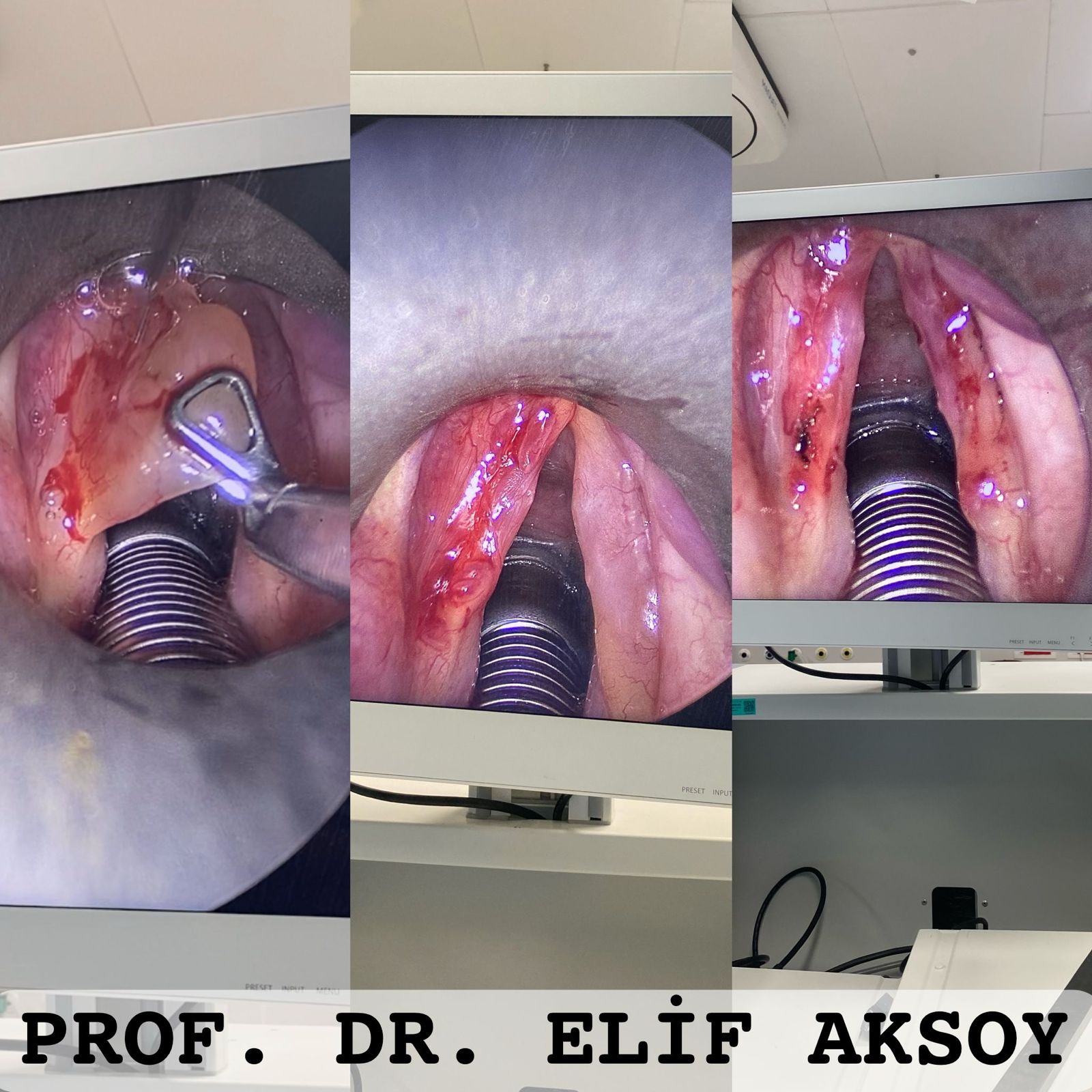
Treatment Methods
1-) Lifestyle Modifications
The most important step in treatment is eliminating the factors causing the edema:
- Quitting or significantly reducing smoking
- Treating reflux and using medications to control stomach acid
- Using the voice correctly and avoiding overuse or strain
These measures can stop the progression or lead to regression of the edema. However, in some cases, additional treatments may be necessary to achieve complete recovery.
2-) Voice Therapy
Voice therapy is especially important for professional voice users (singers, teachers, call center workers, etc.). It teaches correct vocal techniques and helps prevent recurrence of the edema.
3-) Surgical Intervention
If lifestyle changes and voice therapy do not provide sufficient results, a procedure called phonomicrosurgery may be performed. During this surgical procedure, the gelatinous material accumulated on the vocal cords is carefully removed.
- Complete voice rest is recommended after the surgery. Patients should avoid speaking, even whispering, for a few days or weeks.
- Postoperative voice therapy supports the recovery process and helps the patient regain optimal vocal quality.
Conclusion
Reinke’s edema is a common condition, especially among smokers and individuals who use their voice professionally. With early diagnosis and the right treatment approach, you can protect your vocal health. If you notice persistent changes in your voice, hoarseness, or vocal weakness, it is important to consult an ENT specialist.