Transnasal Esophagoscopy (TNE): Comfortable and Sedation-Free Esophageal Examination
Transnasal Esophagoscopy (TNE) is a modern diagnostic method used to examine the esophagus, pharynx, and entrance to the stomach using a thin endoscope through the nose. Unlike traditional gastroscopy, it does not require sedation and is a more comfortable and quicker procedure.
When Is TNE Used?
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and esophageal irritation
- Swallowing difficulties (dysphagia) and esophageal strictures
- Barrett’s esophagus and cancer screening
- Sensation of something stuck in the throat, chronic cough, and hoarseness
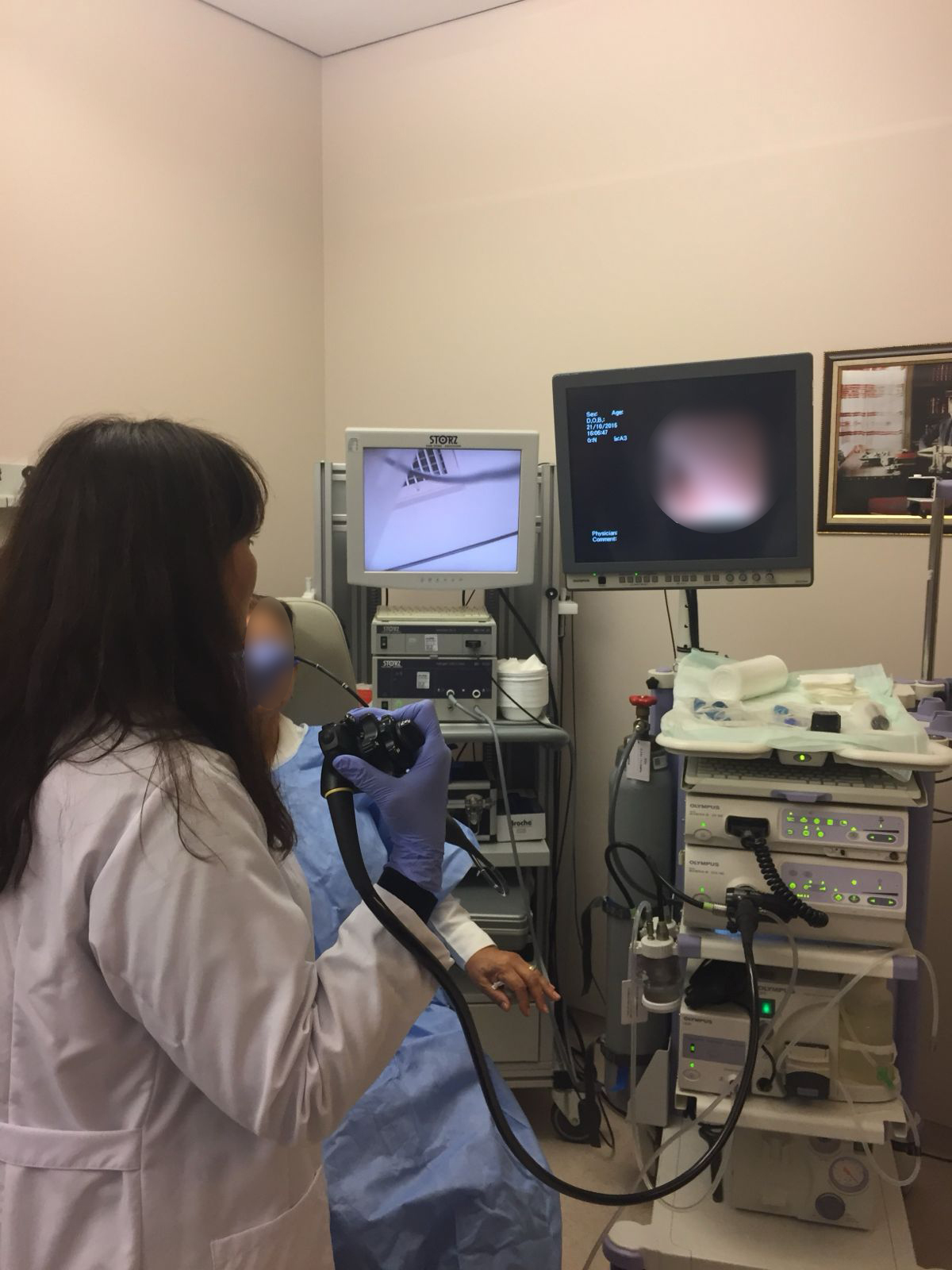
How Is TNE Performed?
An anesthetic spray is applied to the nose.
A thin endoscope is inserted through the nose to examine the esophagus and stomach entrance.
A biopsy can be taken, and the procedure takes 5–10 minutes.
The patient can immediately return to normal daily activities.
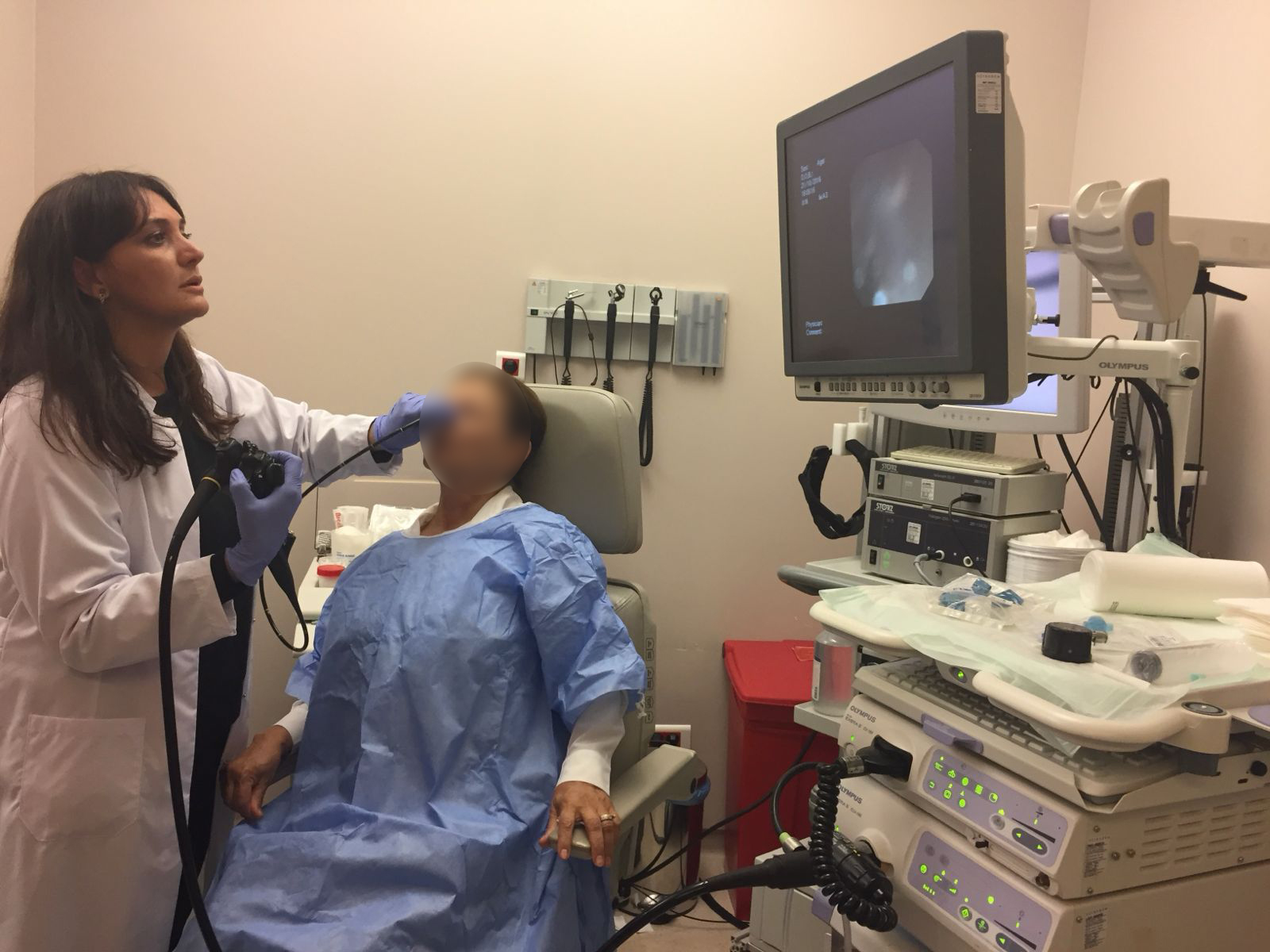
Advantages of TNE
- No need for sedation; the patient remains fully conscious.
- A fast and comfortable procedure with no gag reflex.
- Can be performed on an outpatient basis; no observation period required after the procedure.
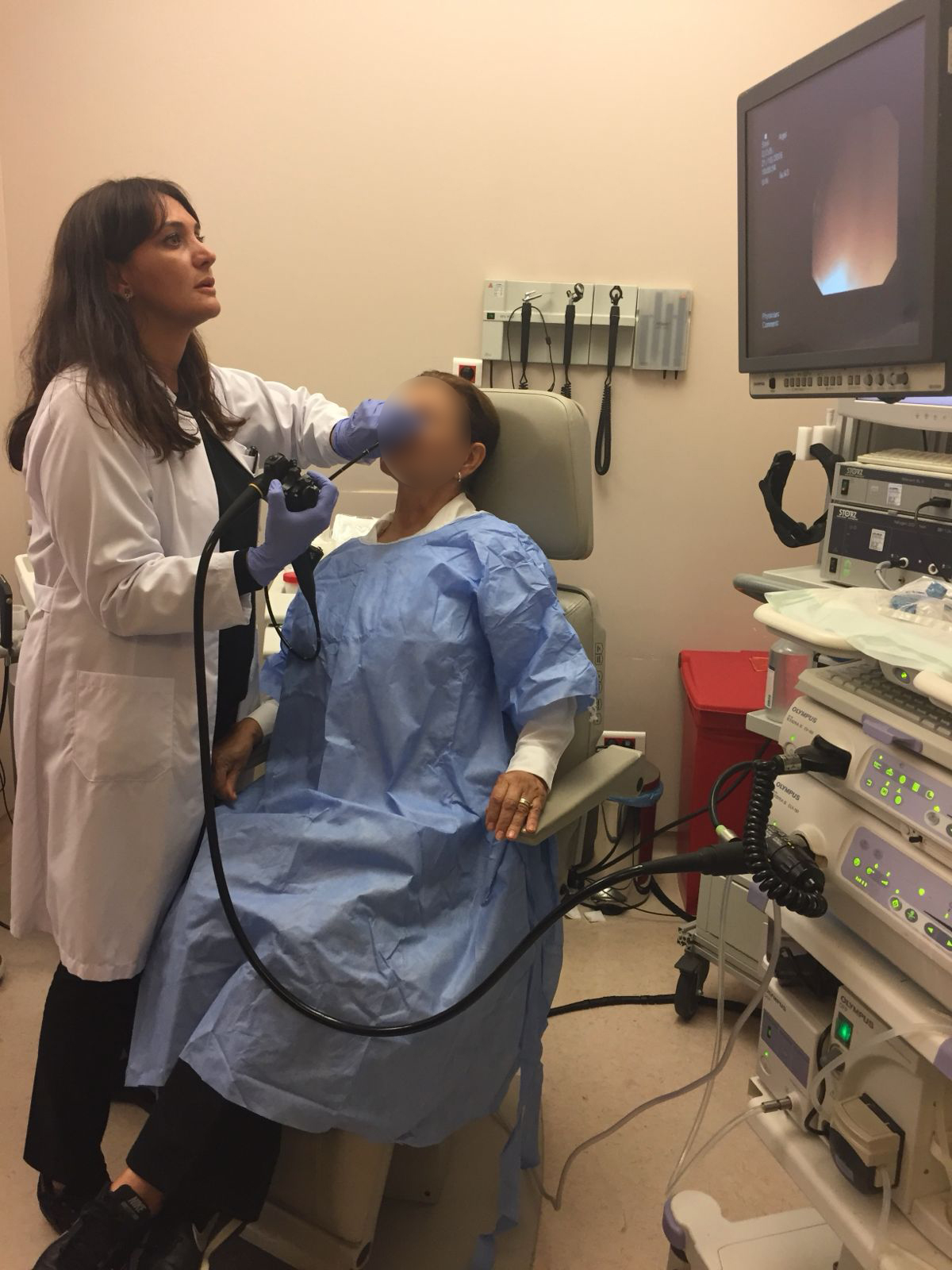
Who Is Not Suitable for TNE?
- Patients with nasal obstruction or nasal passage narrowing
- Patients with large masses or at high risk of severe bleeding
If you are experiencing symptoms related to reflux, difficulty swallowing, or esophageal problems, TNE offers a fast and comfortable solution without the need for sedation.