Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE): A Chronic Immune Disease of the Esophagus
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) is an immune-related condition that causes chronic inflammation of the esophagus. Triggered by allergic mechanisms, this disease is characterized by the abnormal accumulation of white blood cells called eosinophils in the esophagus. EoE can cause symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and the sensation of food getting stuck in the throat.
Causes of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Although the exact cause of EoE is not fully known, it is commonly associated with food allergies, environmental allergens, and genetic predisposition.
- Allergenic foods such as milk, eggs, soy, wheat, and tree nuts
- Environmental allergens such as pollens and house dust mites
- Overreaction of the immune system (autoimmune mechanisms)
- Family history and genetic susceptibility
Symptoms of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Symptoms of EoE may vary by age:
In Adults
- Difficulty swallowing (Dysphagia) – Solid foods getting stuck in the esophagus
- Chest pain – May be mistaken for reflux but is not related to stomach acid
- Sensation of narrowing and food sticking in the esophagus
- Chronic heartburn and reflux-like symptoms
In Children
- Reluctance to eat and feeding difficulties
- Frequent vomiting and stomach discomfort
- Growth retardation and weight loss
How Is Eosinophilic Esophagitis Diagnosed?
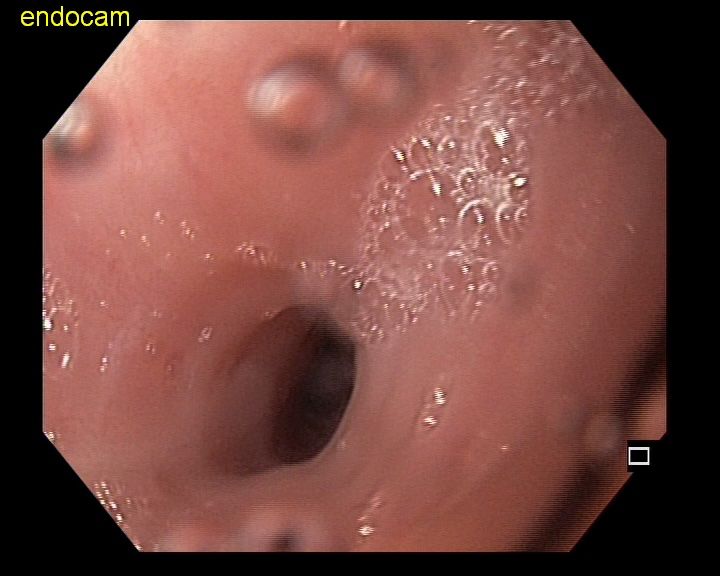
- Endoscopy: Used to visualize the esophagus. In EoE patients, inflammation, rings (trachealized esophagus), or white plaques may be seen on the esophageal wall.
- Biopsy: A sample taken from the esophagus is examined for eosinophil density.
- Allergy Tests: Can be performed to identify food and environmental allergens.
Treatment Methods for Eosinophilic Esophagitis
The primary goal in EoE treatment is to reduce inflammation in the esophagus and control the symptoms.
Dietary Therapy
- An elimination diet that removes food allergens is applied.
- The most common approach is the six-food elimination diet (milk, eggs, soy, wheat, tree nuts, seafood).
Medication Therapy
- Corticosteroids (swallowed steroids) – Used to reduce inflammation in the esophagus.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) – Acid-suppressing medications may help relieve symptoms.
Dilation Therapy
In patients with significant esophageal narrowing, endoscopic dilation (widening) may be performed.
Conclusion
Eosinophilic Esophagitis is a chronic and progressive disease that requires early diagnosis. With appropriate dietary adjustments, medical treatment, and lifestyle changes, symptoms can be effectively managed.


