Endoscopic Swallowing Evaluation
Swallowing is a vital reflex that we often perform unconsciously throughout our lives. This process ensures that food passes safely from the mouth to the stomach and can be impaired in individuals with advanced age, after a stroke, or with neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
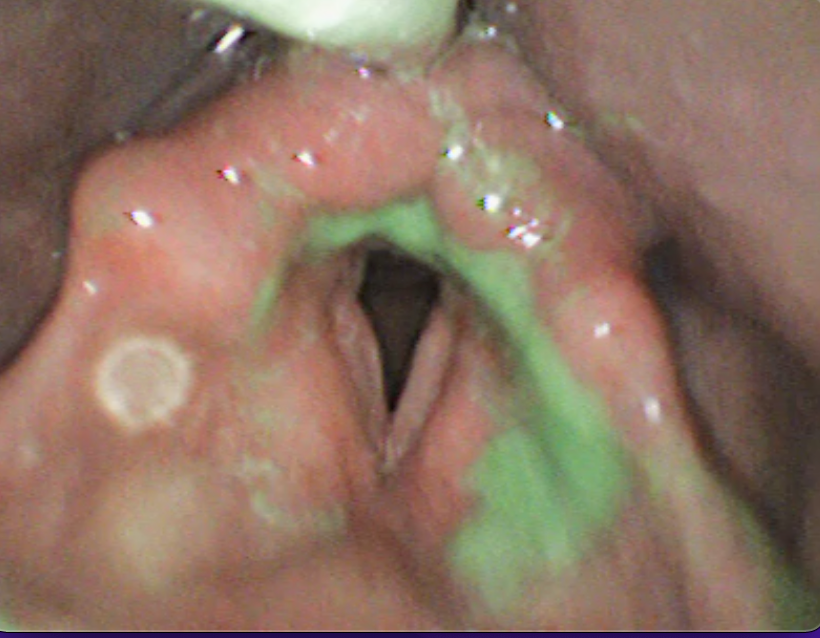
The swallowing process has two main components: airway protection and proper food passage. If a person directs food in the wrong direction during eating, it indicates insufficient airway protection. Endoscopic swallowing evaluation offers a detailed analysis by directly observing how food moves, whether there is any residue, and whether the airway is protected.
How Is Endoscopic Swallowing Evaluation Performed?
During this evaluation, the patient is given foods of various consistencies, colored with green food dye. Using a flexible endoscope, the progression of food during the swallowing process is observed in real-time. The patient’s airway protection reflex is also evaluated. If the person can adequately protect their airway, the next step involves determining the safest swallowing method using different consistencies. The safest swallow is defined as one where the individual does not cough or aspirate food into the airway.
A Speech-Language and Swallowing Disorders Specialist is present during the procedure to guide the patient in performing necessary swallowing maneuvers. This ensures identification of the most comfortable and safest swallowing position for the patient.
Advantages of Endoscopic Swallowing Evaluation
- No radiation exposure: Unlike modified barium swallow studies, this procedure involves no exposure to radioactive material.
- Immediate results: Information obtained during the evaluation is analyzed in real time, enabling a quick and tailored treatment plan.
- Bedside and outpatient applicability: Especially suitable for bedridden patients due to its mobility and ease of application.
- Reduces risk of aspiration pneumonia: By identifying the safest swallowing method, the risk of food entering the lungs is minimized.
- Direct observation of motor and sensory components of swallowing: Includes assessment of velopharyngeal closure, tongue base and hypopharynx anatomy, vocal cord movement, pharyngeal muscle function, and the patient’s ability to clear their own secretions.
Conclusion
Endoscopic swallowing evaluation is a vital diagnostic and follow-up method for patients with swallowing difficulties. It allows comprehensive assessment of both motor and sensory components of swallowing, enhances patient safety, optimizes nutritional intake, and improves overall quality of life.
Endoscopic Swallowing Evaluation
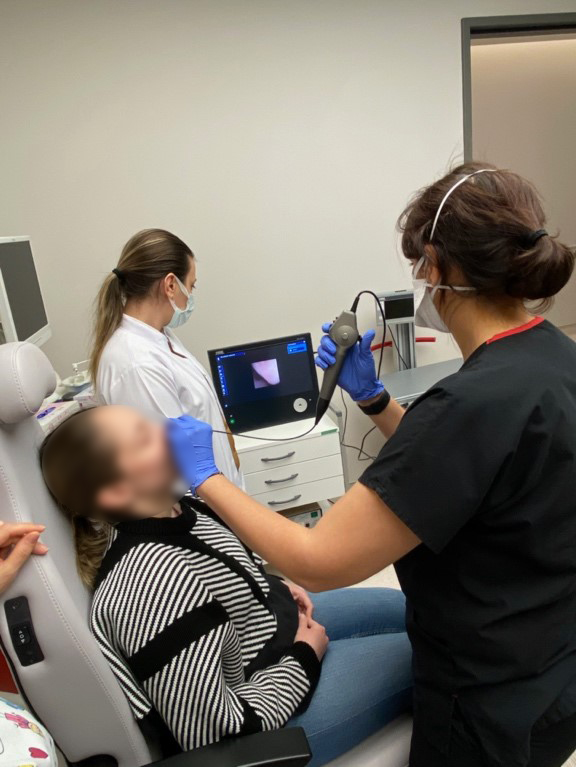
Endoscopic Swallowing Evaluation
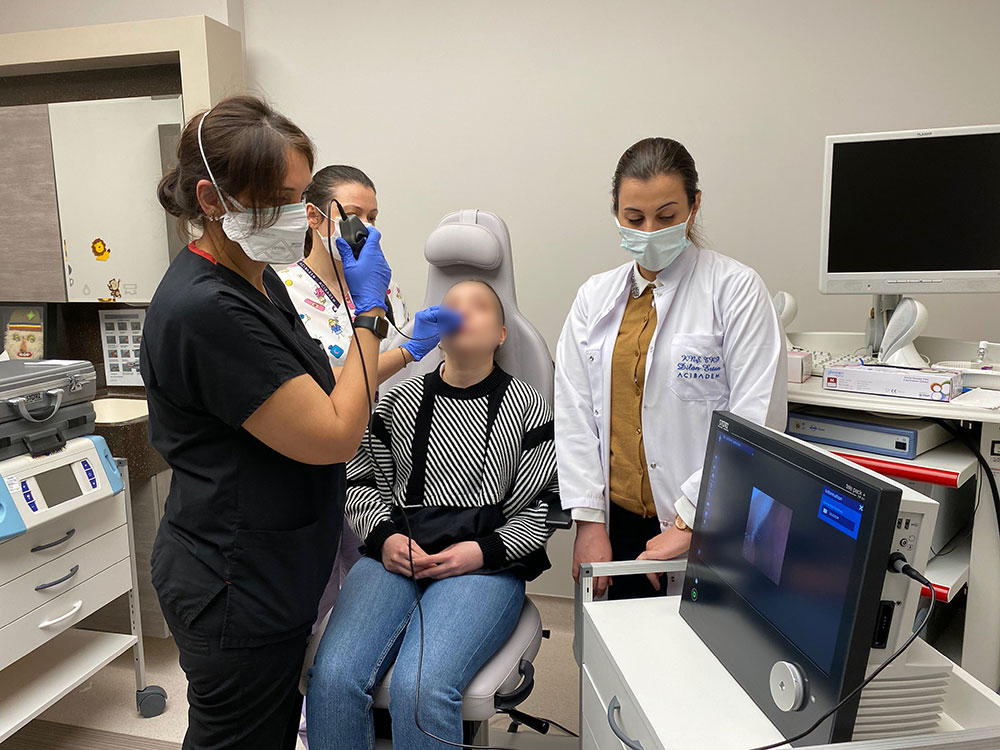
Bedside Endoscopic Swallowing Evaluation

Endoscopic Swallowing Evaluation in Children
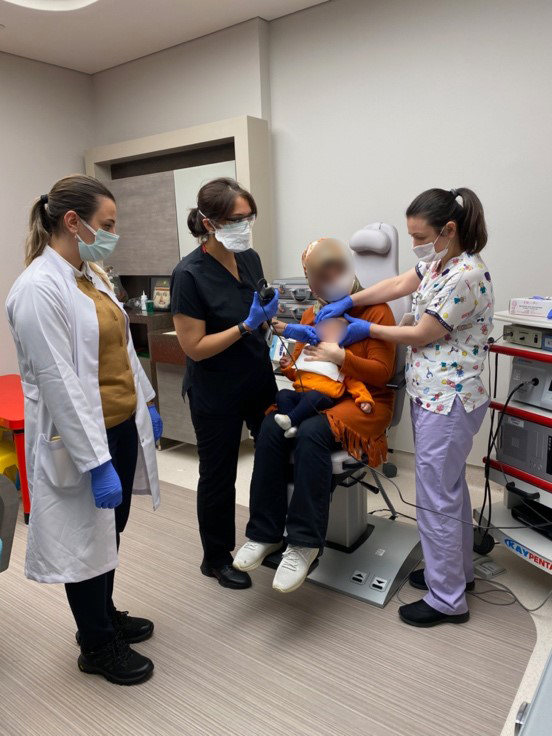
Endoscopic Swallowing Evaluation in Infants
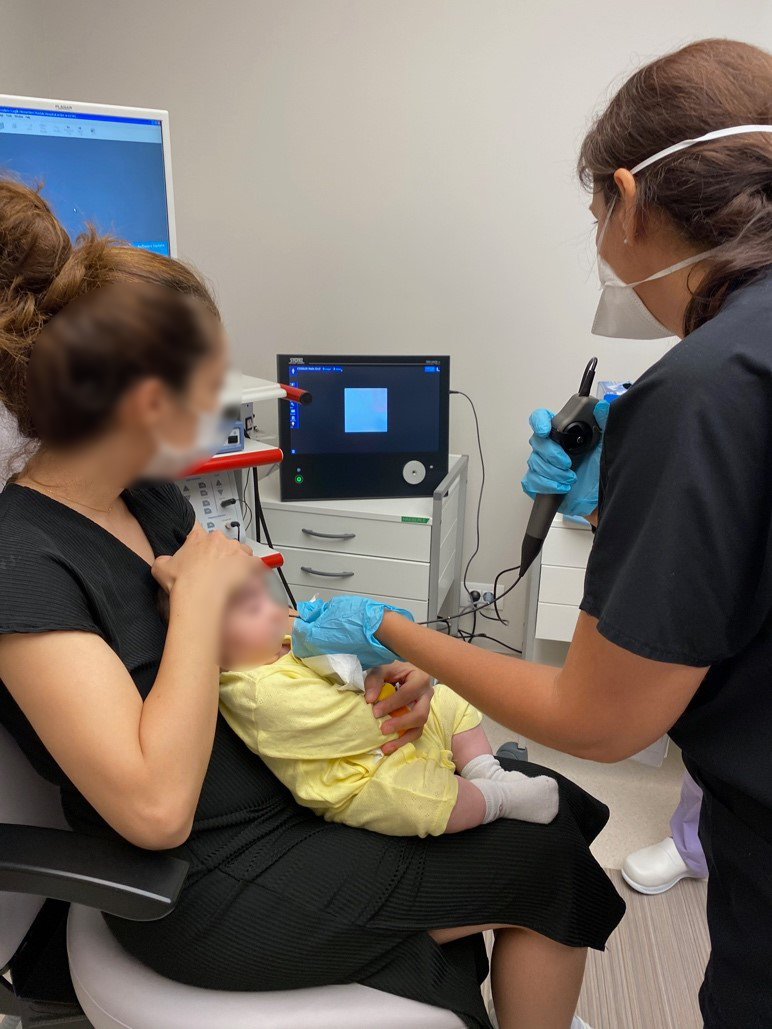
Nectar Penetration and Aspiration
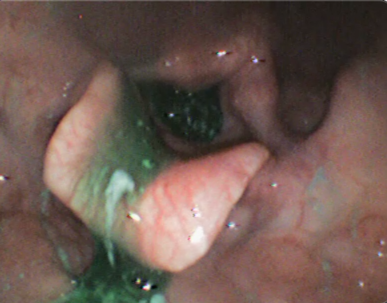
Yogurt Residue