Smoking and Vocal Cord Health: What is Reinke’s Edema?
Prof. Dr. Elif Aksoy
ENT Specialist – Voice and Swallowing Disorders
How Does Smoking Affect Your Vocal Cords?
Smoking can lead to structural and functional damage to the vocal cords. In long-term smokers, chronic irritation of the tissue covering the vocal cords can lead to a condition called Reinke’s edema or polypoid corditis.
This condition not only affects voice quality but may also cause permanent hoarseness and shortness of breath over time.
What is Reinke’s Edema?
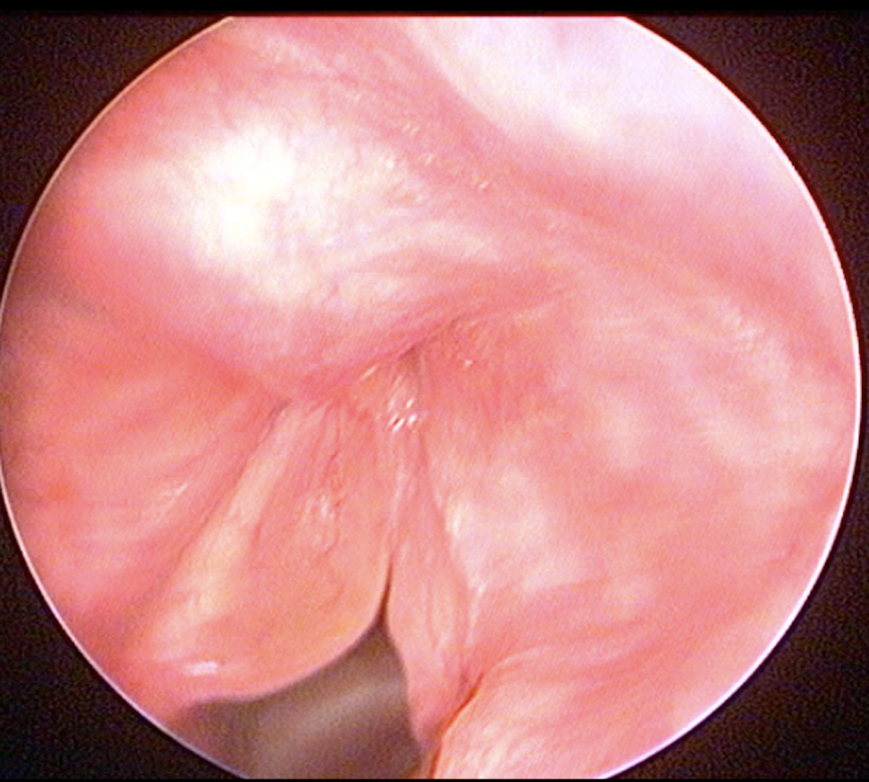
Beneath the surface mucosa of the vocal cords lies a thin layer known as “Reinke’s space.” Due to the effects of smoking, clear, gelatinous fluid gradually accumulates in this area, causing the vocal cords to swell. This condition is called Reinke’s edema. As the condition progresses, fluid accumulation increases, the mucosal structure deteriorates, and the vocal cords take on a polyp-like appearance. This is also referred to as polypoid corditis. It is a chronic irritation-based lesion, typically bilateral.
What Are the Symptoms?
- Persistent and deep hoarseness
- More noticeable voice changes in the morning
- Fatigue while speaking
- Sensation of fullness or irritation in the throat
- Shortness of breath (in advanced cases)
In women who smoke, it is typical for the voice to become deeper and more masculine due to Reinke’s edema. Many complain of being mistaken for a man on the phone.
Diagnosis
- Endoscopic laryngoscopy allows direct visualization of the vocal cords.
- Videolaryngostroboscopy evaluates the vibration of the vocal cords.
- A biopsy may be performed if necessary. Reinke’s edema is not cancer and does not turn into cancer. However, someone who has developed Reinke’s edema due to heavy smoking is at significant risk for laryngeal cancer.
What Are the Treatment Options?
- Quitting Smoking
- Voice Therapy
Proper voice use is taught, and vocal hygiene is promoted.
In early-stage Reinke’s edema, this alone may be sufficient.
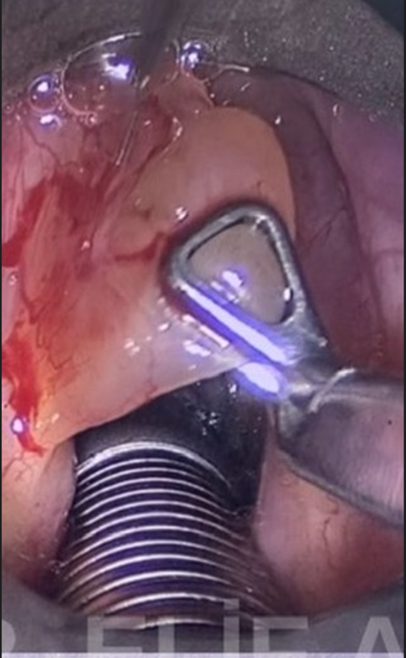
Vocal Cord Microsurgery
With the aid of a microscope and endoscope, the gelatinous content is drained while preserving the mucosal surface.
Postoperative voice therapy significantly improves long-term success rates.
Vocal Cord Microsurgery
Post-Surgery Precautions
- Voice rest (first 5–7 days)
- Avoid smoking and alcohol
- Control of reflux and allergies
- Voice therapy
Your Voice Health Is in Your Hands
Reinke’s edema and polypoid corditis are preventable and treatable conditions. When smoking is stopped and treatment is undertaken with an ENT specialist, the majority of patients regain voice quality and experience improved quality of life.